Generating an SSH keypair in Linux
In order to generate an SSH keypair in Linux, we recommend using the command ssh-keygen.
If system does not see this packet installed, install the latest updates:
- Ubuntu and Debian family
sudo apt-get update && apt-get install openssh-client
- CentOS and Red Hat
sudo yum install openssh-clients
After that, use the following command in terminal:
ssh-keygen
with additional flags:
- -t
rsa authentication key type
- -b
4096 bit length, 2048 if not specified. Available values: 1024, 2048, 4096. The greater the value, the more complicated the key will be.
- -C
user@server name for identification at the end of the file
- -f
~/.ssh/keys/keylocation location of folder with ssh keys
- -N
passphrase, can be omitted if user prefers connecting without additional key security

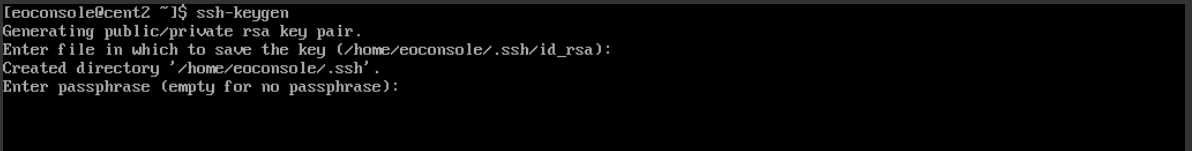
Application will ask for the name of the key. Press Enter for defaults:
id_rsa for private and
id_rsa.pub for public key and passphrase (pressing Enter ignores it).
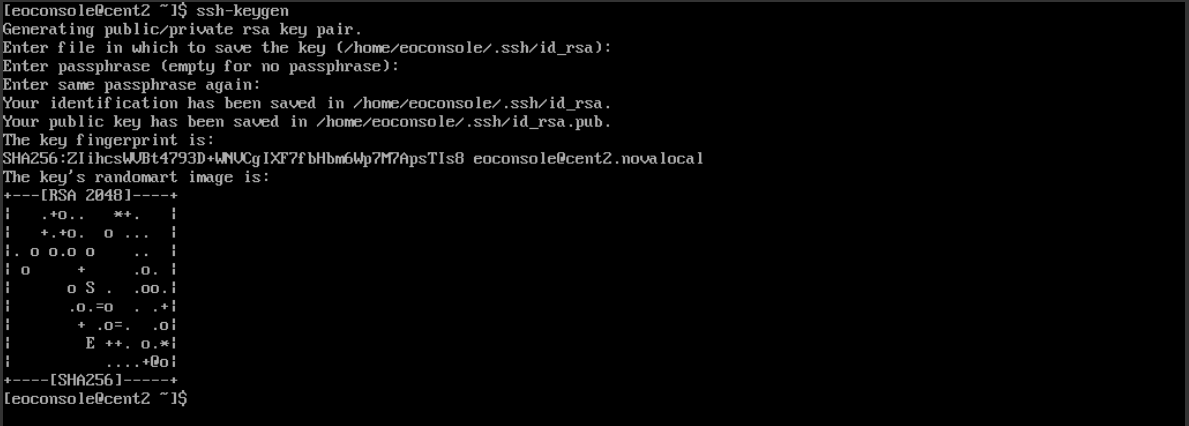
Next, ssh-keygen will show
location, where the keys are saved,
fingerprint of keypair and certain
semi-graphic image as expression of randomness in generating unique key.
To avoid problem with rejecting files due to too open permissions, navigate to the folder containing both keys and enter command:
chmod 600 id_rsa && chmod 600 id_rsa.pub